Blockchain
An Overview of Layer 2 Roll-ups
Over the previous few years, Layer 2 (L2) rollup options have come to the forefront as exercise on the Ethereum community has grown. Exercise and engagement with non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has brought on a surge in Layer 1 (L1) blockchain exercise.
In flip, the demand for blockspace, represented by fuel prices, has elevated. And the time for transaction finality has risen because of the elevated community load.
While the Ethereum Merge set the groundwork for future fuel charge optimisations; it didn’t instantly cut back transaction fuel charges.
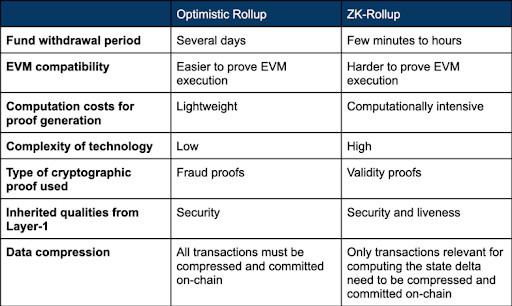
Within the yr between the summer season of 2020 and the height demand in the summertime of 2021 fuel value in Gwei on the Ethereum community elevated by as much as 1300%. The necessity to make transactions quick and reasonably priced spurred the creation of two major types of rollup: Optimistic and Zero-Data (ZK).
Rollups assist take away the computational calls for on the Ethereum community by shifting transaction processing off-chain, changing them right into a single piece of information after which submitting again on Ethereum as a batch to scale back the related value and time.
The large distinction between the 2 is that Optimistic roll-ups utilise fraud proofs, whereas ZK-rollups depend on zero-knowledge proofs to confirm adjustments to the primary chain.
Optimistic and ZK-rollups: Fraud Proofs vs Validity Proofs
Fraud proofs bundle transactions off-chain after which repost them to the L1. After a bundle has been submitted on the L1 there’s a problem interval, throughout which anybody can problem the results of the rollup by computing a fraud proof.
Equally, zero-knowledge proofs batch transactions off-chain and submit them as a single transaction. The place they differ is reasonably than assuming the transactions are appropriate initially, they use a validity proof to immediately show whether or not the transactions are legitimate. As soon as the transactions have been confirmed as legitimate they’re then submitted to the L1.
That is how they derive their respective names – fraud proofs are the place the transactions are checked retrospectively to see if there are any fraudulent transactions, whereas validity proofs are accomplished earlier than the transactions are submitted to the L1.
While there are outstanding tasks for each, they every include their very own respective advantages and disadvantages. Optimistic roll-ups have the benefit that fraud proofs are solely required when there is a matter.
This implies they require much less computational sources and are capable of scale nicely. The difficulty lies with the problem interval. An extended problem interval will increase the probability that any fraudulent transactions are recognized, nonetheless it additionally implies that customers have to attend longer to withdraw their funds.
For main optimistic rollup options, similar to Arbitrum and Optimism, this ready interval can last as long as every week. Alternatively, ZK-rollups have the benefit of all the time reflecting an accurate L2 state. Their downside is that proofs are required for all state transitions, reasonably than solely when they’re contested, which limits scalability. That is additional compounded by the advanced nature and early stage of the know-how.
Regardless of their respective challenges, ZK-rollups are being heralded as the longer term for roll-ups. That is primarily because of the automated era of validity proofs growing the safety of the protocol, the considerably decreased time to withdraw as a consequence of there being no problem interval, and that ZK-rollups boast higher knowledge compression.
For these causes we’ll hone in on the present state of the ZK-rollup house, the most recent improvements and what lies forward sooner or later.
The ZK-Rollup House
As we’ve mentioned, ZK-rollups are predominantly in the point of interest with gamers like zkSync, Starknet, Polygon zkEVM, and Scroll all elevating giant quantities of capital to develop their options regardless of solely StarkNet having launched on mainnet ($780MM in complete).
Every of those tasks have taken their very own angle, differing primarily throughout their rollups knowledge availability technique and their proving algorithm. The information availability technique determines the place the state knowledge of a roll-up is saved, on-chain storage has elevated safety nevertheless it makes use of up block house on the Ethereum community which reduces transaction throughput.
The proving algorithm is the technique of producing a validity proof, which might both be STARK or SNARK.
Each of those algorithms assist builders to relocate computation and storage off-chain, in flip growing scalability. They’re additionally capable of confirm whether or not a consumer has adequate funds and the proper personal key with out having to entry the knowledge itself, thus bettering the safety.
You possibly can learn extra in regards to the technical variations right here. STARKs have the benefit of providing extra scalability, safety and transparency in comparison with SNARKs.
However the downside STARKS have is a bigger proof measurement, which takes longer to confirm, and that SNARKs comparatively solely use 24% of the fuel. Therein for each SNARKS and STARKS now we have the tradeoff between pace and price vs. scalability, safety and transparency.
While many alternative strategies are being explored there may be not but a definitive reply as to one of the best ways to arrange a ZK-rollup. Every configuration brings respective advantages and lots of builders are nonetheless exploring the optimum alternative or mixture for his or her rollup designs.
The Hurdles To Overcome
As we’ve mentioned, ZK-rollups are nonetheless in improvement and there are numerous challenges that must be overcome earlier than blockchain customers are capable of reap their full advantages.
Language compatibility is one such problem; translating EVM-friendly programming languages, similar to Solidity, right into a custom-built language particularly optimised for ZKP may help increase their effectivity, nevertheless it brings with it adoption challenges for builders.
For instance, StarkNet is trying to remedy this with Warp, a Solidity to Cairo (the language of StarkNet’s ZKP) language compiler that appears to robotically convert Solidity into Cairo. Utilizing Warp removes the necessity for builders to rewrite their code in Cairo, making it a a lot smoother course of.
Different challenges embody the secretive nature of tasks, with many going towards the open supply ethos of crypto as a consequence of issues over first-mover benefit and capturing a sticky userbase. Most ZK-rollups have been first launched this yr, highlighting the quantity of labor that’s but to be accomplished within the house.
Lastly, while rollups (each optimistic and zero-knowledge) have the advantages of improved pace and price, it tends to be on the expense of decentralisation.
That is because of the inherent want for sequencers, the actors batching transactions and committing proofs to the L1.
All rollups at present want a centralised sequencer and use upgradeable sensible contracts which can be managed by a single entity. As a result of the house continues to be so early, a central point of interest is usually required for fast fixes to bugs within the code. Add to that the tasks aren’t open sourced, creating one other hurdle for group members to behave as sequencers.
Many tasks have indicated that they plan to decentralize their sequencer features sooner or later, however this can undoubtedly take extra sources and time.
Decentralization Plans
Launching a token and open-sourcing code would be the subsequent steps for lots of the tasks looking for decentralisation. Tokenisation of those providers to generate exercise and decentralise the product is one other space the place we anticipate to see a myriad of various options cropping up as tasks look to create essentially the most scalable, decentralised and energetic L2 in the marketplace.
StarkWare and zkSync are each planning to launch a token and Polygon might doubtlessly use MATIC to assist Polygon’s zkEVM initiative. Token engineering on ZK-rollups is an much more nascent house than the optimistic rollup know-how and discovering an efficient and sustainable mannequin can differentiate and increase adoption.
The Future
zkEVMs are nonetheless of their very early levels and the race is on to launch on mainnet. StarkNet has the primary mover benefit however nonetheless has challenges close to supporting Solidity options as a consequence of using Cairo, leaving room for rivals to make enhancements.
The tasks which can be capable of amass vital consumer bases will appeal to dapp builders, in flip bringing extra dApps to their platform and growing the characteristic set. ConsenSys’ zkEVM is at present shifting to testnet and are focussing particularly on dapp builders for that reason, leveraging instruments like MetaMask, Infura and Truffle in order that they’ll deploy and handle functions as in the event that they have been instantly utilizing Ethereum.
And while now we have mentioned the present gamers within the zkEVM market, different predominant rollup options like Polygon, Optimism and Arbitrum nonetheless command a big market share.
As zkEVM options mature, we may even see these tasks look to transition to validity proofs or hybrid options, leveraging their current consumer bases to draw dapp improvement and preserve their market dominance. Ultimately, the numerous rollup options (and the elevated competitors between them) will proceed to enhance the web3 consumer expertise and introduce platforms for functions to onboard the following era of customers.
Given these threats, we’re not stunned on the secrecy of tasks within the house, however we imagine the true winner will be capable to leverage the effectivity of ZK-rollups and mix it with a seamless developer and consumer expertise to come back out on prime.

